lentil.zernike_compose#
- lentil.zernike_compose(mask, coeffs, normalize=True, order='noll', rho=None, theta=None)[source]#
Create an OPD based on the supplied Zernike coefficients.
- Parameters:
mask (array_like) – Mask defining the extent to compute the Zernike polynomial over. All nonzero entries are included in the result.
coeffs (array_like) – List of coefficients corresponding to Zernike indices (Noll ordering) used to create the OPD.
normalize (bool, optional) – If True (default), the output is normalized according to [1]. If False, the output value ranges [-1, 1] over the mask.
order ({'noll', 'fringe', 'ansi'}, optional) – Zernike ordering scheme. Default is ‘noll’.
rho (array_like, optional) – Radial coordinates of the mask.
rhoshould be 0 at the origin and 1 at the edge of the circle.theta (array_like, optional) – Angular coordinates of the mask in radians.
- Returns:
OPD
- Return type:
ndarray
Examples
Compute a random OPD using the first ten Zernikes:
>>> import matplotlib.pyplot as plt >>> import numpy as np >>> import lentil >>> mask = lentil.circle((256,256), 120, antialias=False) >>> coeffs = np.random.rand(10)*1e-8 >>> opd = lentil.zernike_compose(mask, coeffs) >>> plt.imshow(opd, origin='lower')
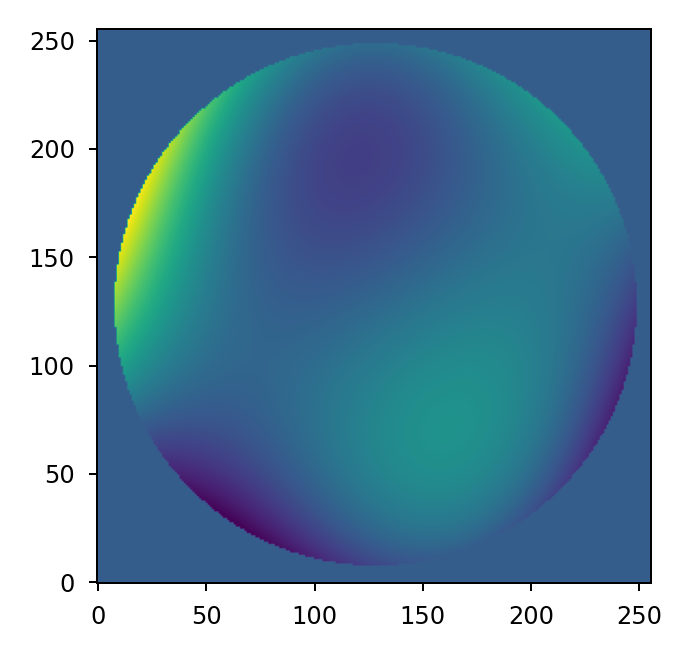
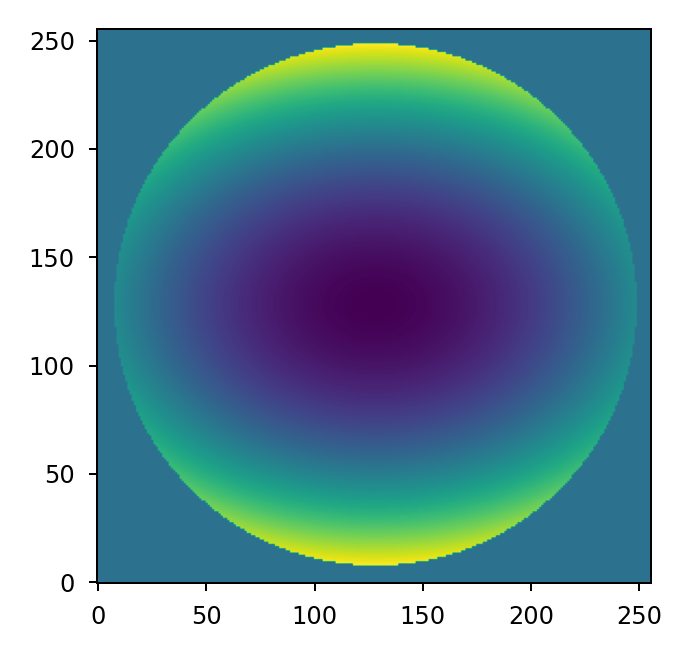
Using the same mask, compute an OPD representing 200 nm focus error (Z4) and -100 nm astigmatism error (Z6):
>>> opd = lentil.zernike_compose(mask, [0, 0, 0, 200e-9, 0, -100e-9]) >>> plt.imshow(opd, origin='lower')
References
[1] Noll, RJ. Zernike polynomials and atmospheric turbulence. J Opt Soc Am 66, 207-211 (1976).